Titanium Abutment Guide: Strength & Compatibility


Comprehensive Guide to the Titanium Abutment
What is a Titanium Abutment?

Titanium Abutments are prefabricated intraoral abutments, secured with screws, and are specifically manufactured for direct connection to an endosseous implant for securing a cemented dental prosthesis. They are suitable for both single-tooth and multiple-tooth restorations. These titanium abutments are meticulously machined from a titanium alloy and affixed to the implant fixture using a titanium screw.
Zirconia and Titanium Abutments: Which One to Use?
The decision between titanium and zirconia abutments depends on the specific clinical scenario, the prosthetic position, and the esthetic requirements. While titanium abutments are preferred for the posterior region and single-unit reconstructions, zirconia abutments are recommended for esthetic zones and special multi-unit reconstructions. Clinicians must weigh the available clinical evidence, individual patient factors, and their own experience when making informed decisions about abutment material.
When to use Titanium Implant Abutments?
The selection of abutment material in implant dentistry is a critical decision that is influenced by several factors, including clinical indication, implant position, and esthetic considerations. Recommendations for the use of titanium and zirconia abutments can be derived from the provided content.
In the posterior regions, titanium abutments are preferred due to their outstanding biocompatibility, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance. Titanium is the biomaterial of choice when it comes to achieving long-lasting and well-documented behavior under functional loading, which applies to both soft and hard tissue. Titanium abutments in particular are considered suitable for single-unit reconstructions in the posterior region, especially when the implant is ideally positioned from a prosthetic point of view.
When to use Zirconia Implant Abutments?

Conversely, in esthetic sites, zirconia dioxide abutments come into focus. They are particularly recommended for the anterior region, where factors such as the thickness of the mucosa and esthetic expectations play an important role. Zirconia abutments, whether standard or customized, are indicated for single-unit reconstructions for esthetic cases with bone-level implants. In addition, zirconia abutments are recommended for use in cemented bridges for multi-unit reconstructions in esthetic zones.
The utilization of CAD/CAM fabrication is emphasized in the context of zirconia abutments. Careful design considerations and precision in the connection to the implant are highlighted as essential elements to ensure long-term success when using zirconia abutments.
Titanium Dental Implants
.jpg)
Titanium dental implants serve as a permanent base for metal-ceramic crowns made of various materials. Over the course of 3-6 months, the titanium implant undergoes osseointegration, a promising process that has also been observed with zirconia fixtures as well. This fusion between bone and titanium enhances the ability of the crown and jaw to withstand significant biting pressures.
Biocompatibility and Osseointegration of Titanium Implants
As previously discussed, titanium implants demonstrate biocompatibility in the majority of patients. Due to its inert nature, titanium rarely has adverse effects on the surrounding gums and teeth. Additionally, these implants tend to osseointegrate effectively into the jawbone, provided sufficient recovery time is allowed.
Titanium remains the predominant choice for abutment materials, due in part to the novelty of zirconia and the compatibility of titanium with the human body. While no implant, including zirconia, guarantees universal success, titanium implants exhibit a notably high success rate. Although there is no one-size-fits-all solution for tooth replacement, titanium remains the first choice in most cases.
Strength of Titanium Implants
Titanium abutments and implants are characterized by their robustness and are resistant to fractures caused by heavy biting or prolonged use. In comparison to ceramic implants such as zirconia or zirconia blends, titanium implants also have a higher flexural strength, meaning they can withstand bending or pushing forces that commonly lead to fractures in more brittle substitute materials. The corrosion resistance and durability of titanium implants are so remarkable that numerous patients report successful results that extend throughout their lifetime.
Aesthetics of Titanium Implants
Titanium implants are similar to metal posts. However, it is important to note that the aesthetics of a titanium implant do not necessarily match the aesthetics of virtually any other dental prosthetic. Abutments are concealed and covered with crowns. This means that the visual success of a replacement depends primarily on the crown, its fit, and its finish, rather than the implant itself.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Titanium Implants
There is a reason that titanium is the established standard in the dental implant industry. Titanium alloys offer osseointegration, cost-effectiveness, strength, and overall biocompatibility, meeting the needs of most implant patients. Titanium implants provide robust support for crowns that mirror the structure of natural teeth and are suitable for a variety of complex crowns and even certain bridges. When the material fuses with the jawbone, it also has the potential to improve bone health and longevity.
Zirconia Dental Implants

Zirconium dioxide, a translucent metal oxide, faithfully mimics the appearance of natural teeth while offering outstanding strength and durability. It is characterized as an exceptionally resistant material for replacing missing teeth. In the fabrication of crowns, this highly robust substance is usually precision-milled using digital scanning parameters.
Zirconia implant abutments are also made from a monolithic zirconia block. Using CAD/CAM technology, they are carefully matched to the shape and specifications of the patient's individual implant requirements prior to the milling process. Edison Medical UAE specializes in custom designs of titanium-based zirconia implant abutments to meet patients' and clinicians' preferences for the benefits of the material, including biocompatibility, aesthetics, and strength.
Biocompatibility and Osseointegration of Zirconia Implants
Zirconia implants contribute to improved long-term oral health and biocompatibility by creating an environment in which bacteria find it difficult to thrive. Additionally, zirconia has significant potential for osseointegration- a process in which the jawbone and biological material successfully integrate or "interlock" with the prosthetics and abutments. This integration leads to prolonged strength and success of the implant. Zirconia, which is frequently used in medical prosthetics, shows promise in seamlessly fusing with the bone.
Strength of Zirconia Implants
Zirconia stands out as one of the most robust technical ceramics available. It is often used for crowns in the posterior region, where the forces caused by grinding and biting are greater. While the fracture toughness and corrosion resistance of zirconia are unmatched among ceramic materials for implants, it falls somewhat short of the durability of titanium implants. When comparing the advantages of zirconia implants with those of titanium implants, it is important to consider this aspect.
Aesthetics of Zirconia Implants
Zirconia excels in the esthetically prominent smile zone. One of the primary benefits of zirconia abutments shared with zirconia crowns, lies in the material's translucent, white hue that closely resembles natural teeth.
As a result, zirconia implants are less conspicuous, especially in patients with thin tissue where the implants might be visible at the gumline. Similar to titanium and metal implants, zirconia is radiopaque, making it detectable on X-rays and scans.
Pros and Cons of Zirconia Implants
With the increasing popularity of zirconia crowns, interest in zirconia implants has also increased. They are characterized by their strength, exceptional aesthetics, and biocompatibility, making them the preferred choice for many implant candidates.
The aesthetic advantages in particular have contributed to dental practices and laboratories opting for zirconia. However, it is also important to consider the drawbacks. While zirconia is robust and capable of osseointegration, it falls slightly short of the strength exhibited by titanium. For those looking for the strongest possible abutment, metal remains the preferred option. In practical terms, concern about the color and shade of the abutment is minimal in most implant cases.
Given that zirconia is still more expensive than its metal counterparts, choosing the industry-standard metal may make more economic sense in many cases. Ultimately, the optimal choice depends on the specific needs of each patient, as dentistry constantly strives to provide personalized solutions for individual cases.
What is a Titanium Base Abutment?
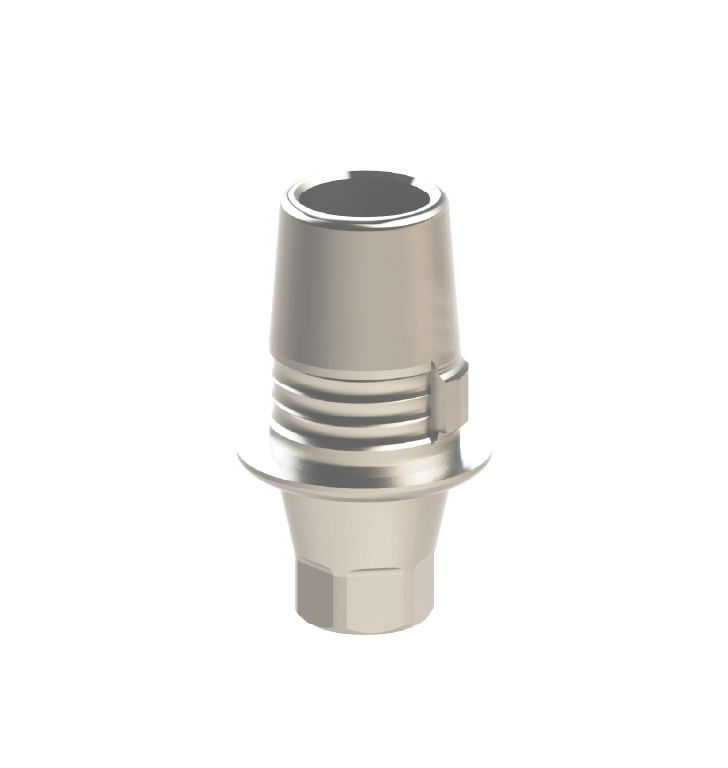

Titanium base abutments have satisfactory mechanical properties and promising clinical behavior, making them a viable alternative for the restoration of dental implants.
One study provides a comprehensive examination of the mechanical and clinical properties of Ti-base abutments, critical components in the restoration of dental implants. These abutments were introduced to solve problems associated with traditional counterparts, such as esthetic concerns and low fracture resistance, and play a vital role in connecting the implant body to implant-supported restorations.
In terms of design, titanium base abutments have specific features that facilitate rapid fabrication of restorations in CAD/CAM systems. Various fabrication techniques, including one and two-piece designs, along with angled screw channels, contribute to their versatility in addressing different clinical scenarios.
The study emphasizes the improved fracture resistance of titanium base abutments compared to all-ceramic counterparts. The incorporation of titanium inserts in zirconia abutments significantly increases fracture resistance, making them a recommended choice for areas subjected to high occlusal forces.
Regarding misfit and torque loss, titanium base abutments show a favorable internal and marginal fit, comparable to other fabrication techniques.
What are Custom Abutments?
Dental laboratories produce customized abutments tailored to the unique tissue ridges of each patient. Crafted from gold, titanium, or zirconium, these abutments offer a precise match for teeth. Even in cases of gum recession, these precisely tailored fixtures accurately replicate the patient's distinctive dentition.
To ensure a precise fit for the customized abutment, the dentist takes an impression or digital scan of the patient's mouth and forwards it to the laboratory. This data not only considers contour and shape but also guarantees an exact match with the profile of the patient's teeth.